Exercise: Sensor Interface¶
Project Setup¶
TODO: this needs more thinking
Problem: Polymorphic Thermometer Usage¶
ConstantSensor and RandomSensor are completely unrelated -
they don’t share a common base class. They just look similar. This
programming technique, Duck Typing, is heavily used in dynamic
languages such as Python (see
Abstract Base Classes (abc), And Duck Typing). It is
not appropriate in a strongly tyoed language like C++ though, as we
will see.
The following program uses an instance of each in an array of a hypothetical interface/base class to measure two temperature points. It calculates the average of both points, and outputs that.
#include <sensor-const.h>
#include <sensor-random.h>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
ConstantSensor cs(42.7);
RandomSensor rs(7, 42);
Sensor* sensors[2];
sensors[0] = &cs;
sensors[1] = &rs;
double sum = 0;
unsigned int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
count++;
sum += sensors[i]->get_temperature();
}
double avg = sum/count;
std::cout << avg << std::endl;
return 0;
}
The Exercise¶
Download the program into the
bin/directory, and register it with that directory’sCMakeLists.txtfile:In addition to the program, download two tests into the
tests/directory, and register them with that directory’sCMakeLists.txtfile:#include <sensor-const.h> #include <gtest/gtest.h> TEST(sensor_const_suite, is_a_sensor) { ConstantSensor cs(36.4); Sensor* s = &cs; // <--- ConstantSensor is-a Sensor // avoid "unused' warning (void)s; }
#include <sensor-random.h> #include <gtest/gtest.h> TEST(sensor_random_suite, is_a_sensor) { RandomSensor rs(36.4, 42.3); Sensor* s = &rs; // <--- ConstantSensor is-a Sensor // avoid "unused" warning (void)s; }
It won’t build
Add the missing
Sensorinterface (create a filesensors/sensor.hto contain it), and make the program compile and run. In UML, the new sensor hierarchy would look like follows: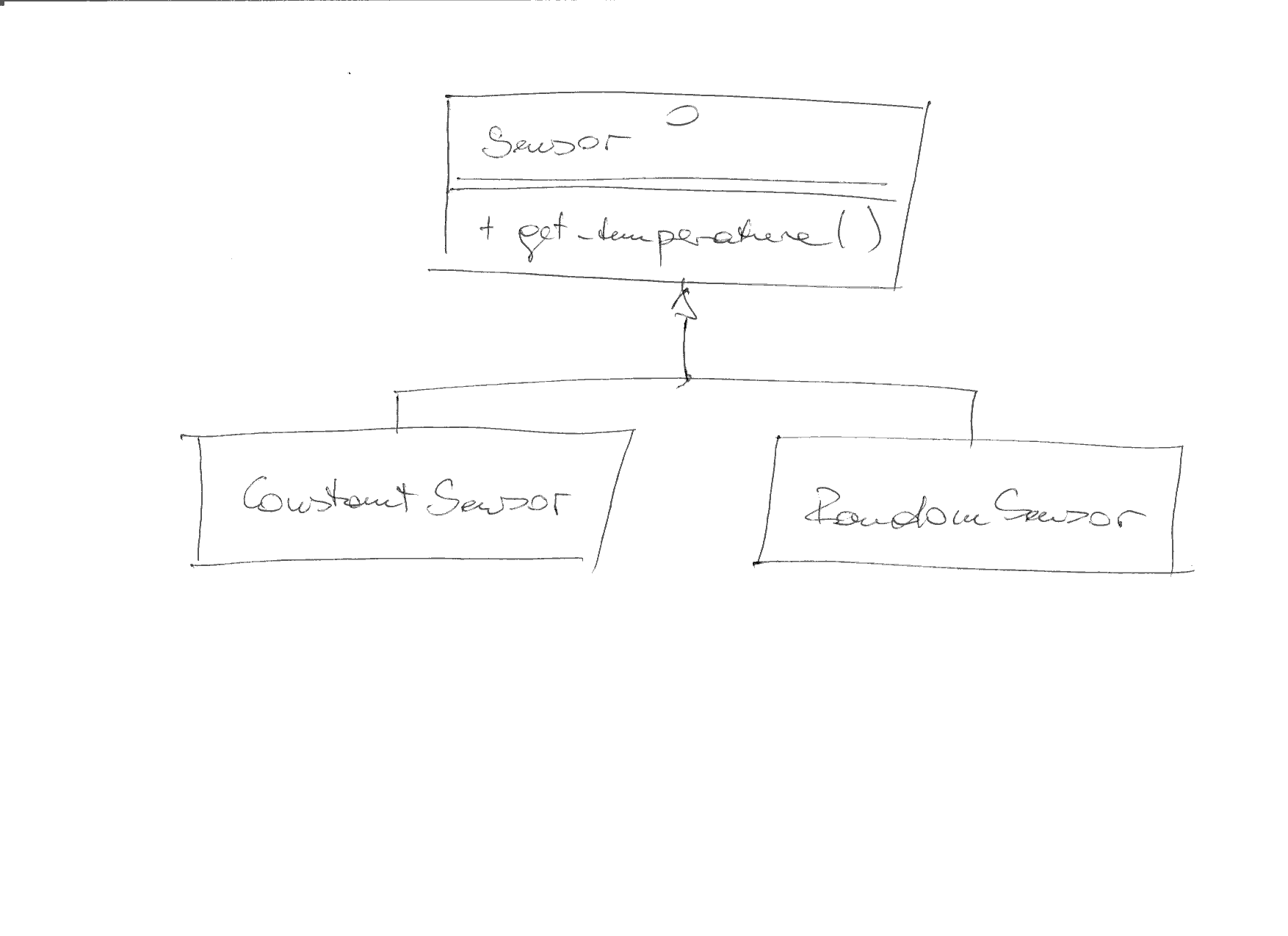
Run the program
$ ./bin/cxx-exercises-sensors-avg 27.5731
Run the tests
$ ./tests/cxx-exercises-sensors-core--suite Running main() from /home/jfasch/work/jfasch-home/googletest/googletest/src/gtest_main.cc [==========] Running 4 tests from 2 test suites. [----------] Global test environment set-up. [----------] 2 tests from sensor_const_suite [ RUN ] sensor_const_suite.basic [ OK ] sensor_const_suite.basic (0 ms) [ RUN ] sensor_const_suite.is_a_sensor [ OK ] sensor_const_suite.is_a_sensor (0 ms) [----------] 2 tests from sensor_const_suite (0 ms total) [----------] 2 tests from sensor_random_suite [ RUN ] sensor_random_suite.basic [ OK ] sensor_random_suite.basic (0 ms) [ RUN ] sensor_random_suite.is_a_sensor [ OK ] sensor_random_suite.is_a_sensor (0 ms) [----------] 2 tests from sensor_random_suite (0 ms total) [----------] Global test environment tear-down [==========] 4 tests from 2 test suites ran. (0 ms total) [ PASSED ] 4 tests.
