Doubly Linked Lists (Slideshow)#
See LDD3 for something much more comprehensive.
See Kernel Documentation for something much more comprehensive.
Big Picture#
(Stolen from LDD3)
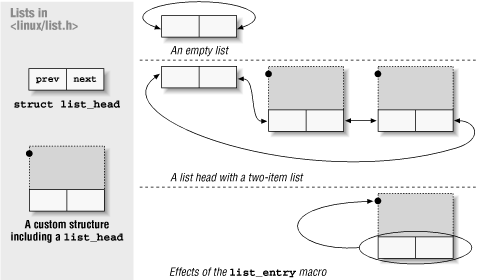
List Head#
#include <linux/list.h>
struct list_head some_list;
/* in some init function ... */
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&some_list);
Pointers to head and tail
Used as entry into list
Rest of list nodes are usually embedded into payload structures
struct payload {
int some_data;
struct list_head node;
};
Insert a Node#
Add one node after another regular node
struct payload* new_payload = ...; // allocate?
struct payload* existing_payload = ...; // already in list
list_add(&new_payload->node, &existing_payload->node);
Prepend: add after head of list
struct payload* new_payload = ...; // allocate?
list_add(&new_payload->node, &some_list);
Append: add before tail member of list_head
struct payload* new_payload = ...; // allocate?
list_add_tail(&new_payload->node, &some_list);
Iteration, and Getting a Node’s Container#
List iteration is error prone ⟶
list_for_each()macroCursor variable is of type
struct list_head⟶ need to access containing structure
struct list_head* run;
list_for_each(run, &some_list) {
struct payload* run_payload = list_entry(run, struct payload, node);
// do something with payload
}
Note
Do not modify a list while iterating!
Emptying a List#
To empty a list, best use a
whileloop untillist_empty()is trueCall
list_del()to removelist_first_entry()in each iteration
while (! list_empty(&some_list)) {
struct payload* a_payload = list_first_entry(&some_list, struct payload, node);
list_del(&payload->node);
// deallocate?
}
